Search for a doctor or hospital in your network.

Search for a doctor or hospital in your network.

Get News & Updates Directly To Your Inbox
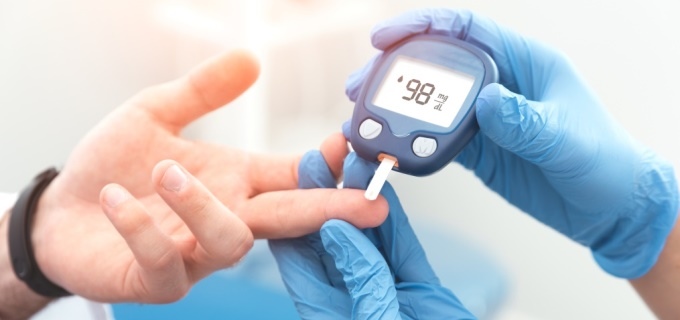
 Most of the food we eat is turned into glucose (sugar). Our bodies use this sugar to fuel our cells with the energy they need to work the right way. It’s a fine balance, though. When blood sugar levels are higher than they should be, it can put a person at risk for a serious long-term health issue — diabetes.
Most of the food we eat is turned into glucose (sugar). Our bodies use this sugar to fuel our cells with the energy they need to work the right way. It’s a fine balance, though. When blood sugar levels are higher than they should be, it can put a person at risk for a serious long-term health issue — diabetes.The pancreas is an organ that lies near the stomach. It works to keep glucose levels under control. It also makes insulin, a hormone that helps glucose get into our cells. In someone with diabetes, the body doesn't make enough insulin or can't use insulin the way it should. As a result, an unhealthy level of sugar builds up in the blood.
The best defense against the diabetes is to educate yourself about the disease. Know how to take care of yourself if you are diagnosed with the disease.
Originally published 11/23/2015; Revised 2019, 2022, 2024
Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Montana, a Division of Health Care Service Corporation,
a Mutual Legal Reserve Company, an Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association
© Copyright 2026 Health Care Service Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Verint is an operating division of Verint Americas, Inc., an independent company that provides and hosts an online community platform for blogging and access to social media for Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Montana.
![]() File is in portable document format (PDF). To view this file, you may need to install a PDF reader program. Most PDF readers are a free download. One option is Adobe® Reader® which has a built-in screen reader. Other Adobe accessibility tools and information can be downloaded at https://www.adobe.com/trust/accessibility.html.
File is in portable document format (PDF). To view this file, you may need to install a PDF reader program. Most PDF readers are a free download. One option is Adobe® Reader® which has a built-in screen reader. Other Adobe accessibility tools and information can be downloaded at https://www.adobe.com/trust/accessibility.html. ![]()
![]() You are leaving this website/app ("site"). This new site may be offered by a vendor or an independent third party. The site may also contain non-Medicare related information. Some sites may require you to agree to their terms of use and privacy policy.
You are leaving this website/app ("site"). This new site may be offered by a vendor or an independent third party. The site may also contain non-Medicare related information. Some sites may require you to agree to their terms of use and privacy policy.
Powered by Verint